Hard water is a common issue affecting millions of households, yet many people underestimate its far-reaching impacts. As an expert who has extensively researched this topic, I’m here to shed light on the surprising ways hard water influences both your living space and your well-being.
Let’s explore the hidden effects of those mineral-rich droplets flowing from your taps.
1. The Skin-Drying Culprit
That tight, itchy feeling after a shower? Hard water might be the unexpected cause.
The high mineral content disrupts your skin’s natural barrier, leading to a host of dermatological issues.
When you wash with hard water, minerals interact with soaps and cleansers, forming a stubborn residue that clings to your skin even after rinsing. This residue clogs pores, exacerbates conditions like eczema, and contributes to overall skin dryness and irritation.
A study in the International Journal of Dermatology revealed that children living in hard water areas had a 50% higher risk of developing eczema compared to those in soft water regions. The minerals in hard water can also alter your skin’s pH balance, potentially increasing sensitivity and inflammation.
To combat these effects, use a chelating shampoo once a week to remove mineral buildup, and apply a moisturizer immediately after bathing to lock in hydration. These simple steps can make a significant difference in maintaining healthy, comfortable skin despite hard water challenges.
2. The Energy Bill Inflator
One of the most costly effects of hard water is its impact on energy consumption. As limescale builds up in water heaters and pipes, it acts as an insulator, reducing heat transfer efficiency.
Your appliances have to work harder and use more energy to heat water to the desired temperature.
The Water Quality Association reports that just a 1/4-inch of limescale buildup can decrease the efficiency of water heaters by up to 40%. Over time, this increased energy usage leads to significantly higher utility bills.
A study by the U.S. Department of Energy estimated that water heating accounts for about 18% of a home’s energy use, making the impact of hard water on energy efficiency a substantial concern.
Your water heater, coated in limescale, struggles to heat water efficiently, consuming more energy in the process. This inefficiency hits your wallet and increases your home’s carbon footprint.
Regular maintenance and descaling can help mitigate these effects, potentially saving you hundreds of dollars annually on energy costs.
3. The Plumbing System’s Silent Enemy
Hard water’s effects extend beyond visible scale on fixtures – it causes severe damage to your home’s plumbing infrastructure. As mineral deposits accumulate inside pipes, they restrict water flow and increase pressure on the system.
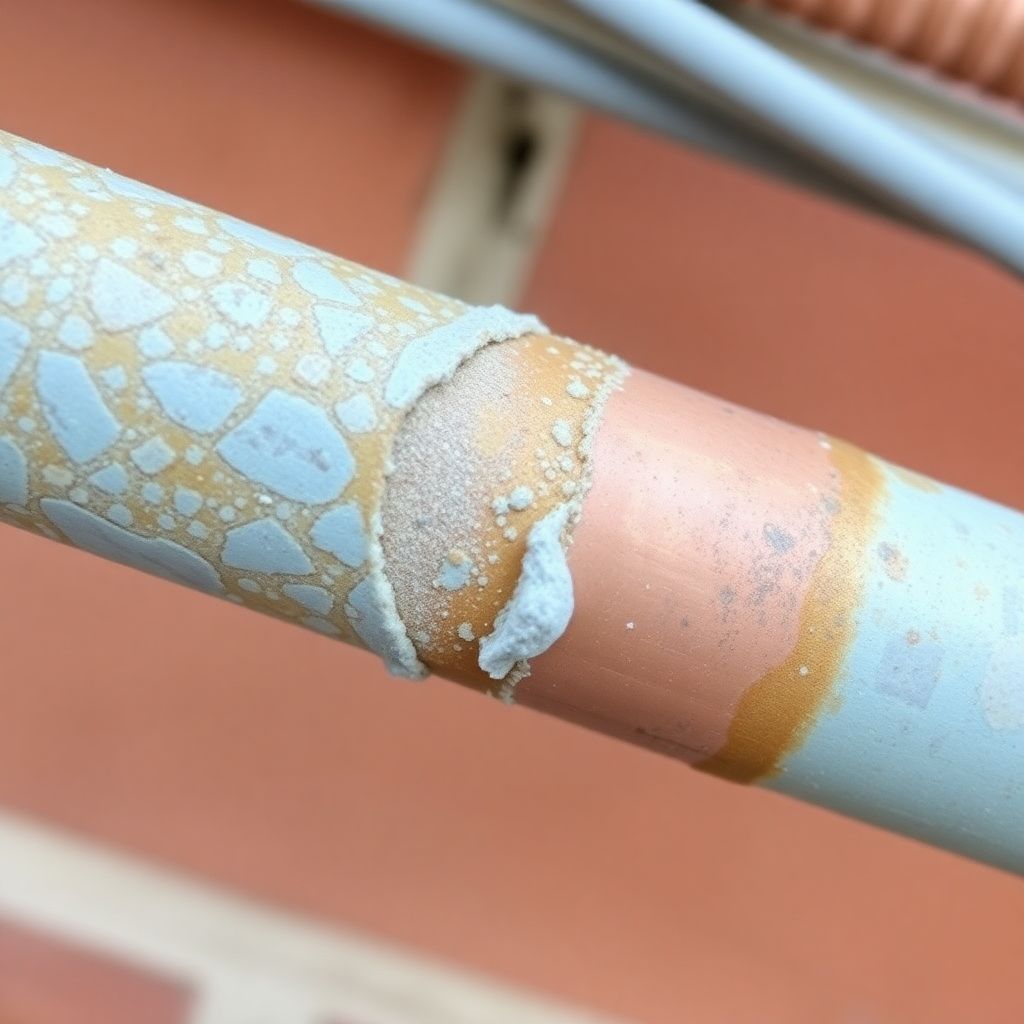

This can lead to leaks, pipe bursts, and even finish system failures.
A report from the Water Quality Research Foundation found that hard water can reduce the lifespan of pipes by up to 50%. Additionally, appliances like water heaters, washing machines, and dishwashers connected to hard water supplies had a 30-50% shorter lifespan compared to those using soft water.
Your plumbing system, much like the circulatory system in your body, suffers when mineral deposits accumulate. These deposits restrict flow, increase pressure, and can lead to costly emergencies.
Regular maintenance and the use of water softeners can help mitigate these damaging effects, potentially saving you thousands in repair costs over the years.
4. The Nutrient Absorption Disruptor
While minerals in hard water are often touted as useful for health, they may actually interfere with your body’s ability to absorb certain nutrients. The high levels of calcium in hard water can bind with minerals like iron and zinc in your digestive tract, potentially leading to deficiencies over time.
A study published in the Journal of Nutrition found that people consuming hard water had lower absorption rates of certain minerals compared to those drinking soft water. This interaction between water hardness and nutrient absorption highlights the complex relationship between water quality and overall health.
The excess minerals in hard water can interfere with your body’s ability to absorb essential nutrients from your diet. This is particularly concerning for people with already compromised nutrient absorption or those at risk for deficiencies.
While hard water alone is unlikely to cause severe nutritional issues, it’s an important factor to consider in your overall health strategy.
5. The Hair Health Saboteur
Hard water has a significant and often overlooked effect on your hair health and appearance. The minerals in hard water react with shampoo, reducing its lathering ability and leaving a residue on your hair strands.
This residue makes your hair feel dry, look dull, and become more prone to breakage.
Research published in the International Journal of Trichology found that hard water can lead to decreased hair strength and elasticity. Furthermore, it can exacerbate conditions like dandruff and scalp irritation.
For people who color their hair, hard water causes faster fading and altered color results because of mineral buildup on the hair shaft.
Your hair, exposed to hard water, becomes stripped of its natural oils and coated with a dull, lifeless residue. This affects appearance but can lead to long-term damage and increased hair loss.
To combat these effects, use a clarifying shampoo once a week to remove mineral buildup, and consider investing in a shower head filter to reduce water hardness.
6. The Gut Health Influencer
Emerging research suggests that hard water may have an unexpected impact on gut health and the microbiome. The high mineral content, particularly calcium and magnesium, can alter the pH balance in your digestive system, potentially affecting the growth and composition of useful gut bacteria.
A study published in the journal Environmental Science & – Technology found that the mineral content in drinking water could influence the diversity of gut microbiota. While more research is needed, this finding opens up new avenues for understanding the far-reaching effects of water quality on overall health.
The minerals in hard water may influence which bacteria flourish in your digestive system, potentially impacting your overall health. This connection between water hardness and gut health adds another layer of complexity to the importance of water quality in our daily lives.
For those with sensitive digestive systems or existing gut health issues, considering water quality might be an important step in managing overall health.
7. The Environmental Impact Multiplier
The effects of hard water extend beyond personal health and home maintenance to broader environmental concerns. The increased use of cleaning products and detergents necessitated by hard water leads to higher levels of chemical runoff into water systems.

Additionally, the reduced efficiency of appliances results in increased energy consumption and associated carbon emissions.
A report from the European Commission estimated that softening hard water could reduce CO2 emissions by up to 10% in some households. Furthermore, the production and disposal of water softeners and descaling agents contribute to environmental waste.
Hard water in your home sets off a chain reaction that affects your immediate environment and contributes to larger ecological issues. From increased chemical use to higher energy consumption, the environmental impact of hard water is a often overlooked aspect of water quality discussions.
Addressing hard water issues at home can contribute to broader environmental conservation efforts.
Key Takeaways:
-
- Hard water exacerbates skin conditions and leads to dry, itchy skin.
-
- Limescale buildup from hard water significantly reduces the efficiency of water heaters and appliances, increasing energy costs.
-
- Hard water shortens the lifespan of your plumbing system and water-using appliances.
-
- The minerals in hard water may interfere with nutrient absorption in your body.
-
- Hard water negatively impacts hair health, leading to dryness, dullness, and increased breakage.
-
- Emerging research suggests hard water may influence gut health and microbiome diversity.
-
- The effects of hard water extend to environmental concerns, including increased chemical runoff and energy consumption.
People Also Asked
What is considered hard water?
Water is considered “hard” when it contains high levels of dissolved minerals, primarily calcium and magnesium. The hardness is typically measured in grains per gallon (gpg) or parts per million (ppm).
Water with more than 7 gpg or 120 ppm is generally considered hard.
How do I know if I have hard water?
Signs of hard water include soap scum on fixtures, difficulty lathering soap, dry skin and hair after showering, spotty dishes, and scale buildup on appliances. You can also purchase home test kits or have your water professionally tested to decide its hardness level.
Can hard water make you sick?
Hard water is generally not considered harmful to human health. However, it can exacerbate certain skin conditions and may interfere with nutrient absorption.
Some studies suggest it might have a protective effect against cardiovascular disease, but more research is needed.
How does hard water affect appliances?
Hard water causes scale buildup in appliances, reducing their efficiency and lifespan. This is particularly noticeable in water heaters, washing machines, and dishwashers.
The scale can clog pipes, reduce water flow, and increase energy consumption.
Is it safe to drink hard water?
Drinking hard water is generally safe and may even provide small amounts of useful minerals like calcium and magnesium. However, some people find that it affects the taste of water and beverages made with it.
How can I soften hard water at home?
There are several methods to soften water at home, including:
-
- Installing a whole-house water softener system
-
- Using a water softener salt
-
- Installing a water conditioner
-
- Using a shower head filter for bathing
Does boiling water remove hardness?
Boiling water does not remove hardness. In fact, it can increase the concentration of dissolved minerals as water evaporates.
However, boiling can help remove temporary hardness caused by bicarbonates.
Can hard water cause hair loss?
While hard water doesn’t directly cause hair loss, it can contribute to hair damage, dryness, and breakage. This can make existing hair loss issues more noticeable and may exacerbate conditions that lead to hair thinning.
How does hard water affect laundry?
Hard water makes it difficult for detergents to lather and clean effectively. It can leave mineral deposits on clothes, making them feel stiff and look dull.
Over time, it can also cause fabric to wear out faster.
Are there any benefits to hard water?
Some studies suggest that the minerals in hard water, particularly magnesium and calcium, may have a protective effect against cardiovascular disease. Hard water can also contribute small amounts of these minerals to your diet.
However, the potential drawbacks often outweigh these benefits for most households.
